Free Shipping For Orders Over 100 Riyal
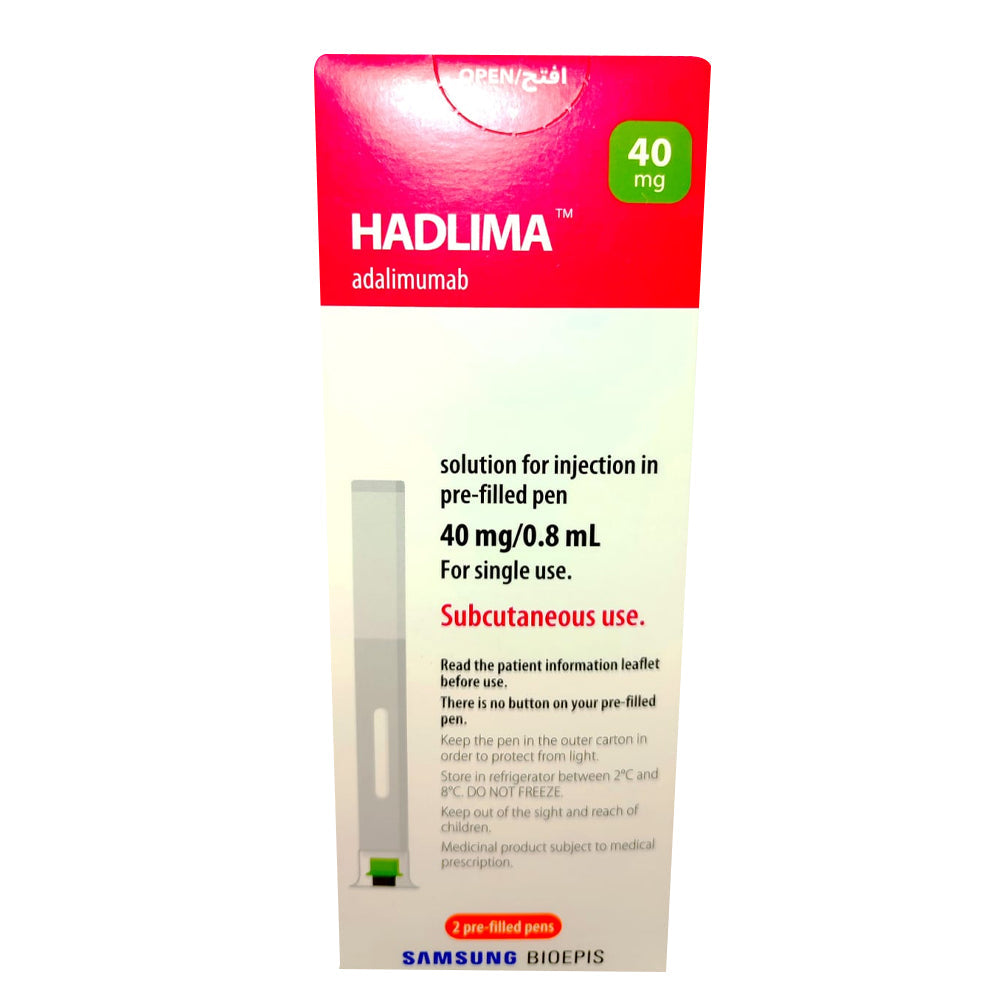
Hadlima 40 Mg 2 Pen
-
1,889.10 SR

-

-
1,889.10

Couldn't load pickup availability
Description
xWhat is Hadlima?
A drug containing the active substance adalimumab, a monoclonal antibody made from one of the body's cells capable of dealing with exotic proteins in the body.
The active substance adalimumab can recognize and bind to certain proteins, whose levels increase with some inflammatory diseases.
What is Hadlima used for?
Hadlima uses include:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
-
Enthesitis-related arthritis.
-
Psoriasis arthritis.
-
Ankylosing spondylitis.
-
Crohn's disease.
-
Ulcerative colitis.
-
Psoriasis.
-
Hidradenitis suppurative.
-
Uveitis.
Hadlima for arthritis
Hadlima is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, preventing damage, and improving joint function in cases of moderate or severe arthritis, and can be used alone or alongside other rheumatoid arthritis medications.
Hadlima also helps with the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, especially moderate or severe in patients 4 years of age or older.
Hadlima for colitis
Hadlima helps alleviate moderate or severe Crohn's disease, especially with the patient not responding to traditional treatment.
Â
The drug also helps treat moderate or severe ulcerative colitis, especially for patients who have not responded well to immunosuppressive drugs.
Hadlima for psoriasis
Hadlima is prescribed for the treatment of moderate or severe plaque psoriasis and is used only with the patient's monitoring and follow-up with the doctor periodically.
How to use Hadlima?
-
Hadlima is used following the doctor's directions.
-
Hadlima is used by subcutaneous injections.
-
The usual dose is 40 mg every two weeks and can be increased as needed at the doctor's discretion.
-
Treatment of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis begins with a dose of 160 mg on one or two days, 80 mg after two weeks, 40 mg after two weeks, and the patient resumes on that dose once a fortnight, which is determined by the doctor.
-
The dose of treatment for psoriasis and uveitis begins at 80 mg, and according to the patient's response, the dose may be reduced to 40 mg or continue as it is.
Hadlima side effects
Hadlima may cause some side effects, such as:
-
Pain, redness, or swelling in the injection site.
-
Common Cold.
-
Runny nose.
-
Sore throat
-
Ear pain.
-
Bleeding gums.
-
Headache.
-
Dizziness.
-
Nausea and vomiting.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
fatigue.
-
chest pain.
Â
The drug may cause serious side effects, the doctor should be consulted as soon as they appear, such as:
-
Signs of infection, such as high temperature, tooth or gum problems, pain during urination, or blood in the urine.
-
Signs of tuberculosis, such as persistent cough, weight loss, fever, and lethargy.
-
Signs of a blood clot, such as swelling, redness, or warmth in one area of the leg or arm.
-
Signs of allergies, such as chest tightness, shortness of breath, swelling of the tongue and lips, or rashes.
Hadlima use precautions
The doctor should be consulted before using Hadlima, especially in the case of:
-
infection.
-
History of TB.
-
Carrier of hepatitis B virus, or suffer from it.
-
suffer from or have been infected with a fungal infection.
-
Blood disorders.
-
Serious heart disease.
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
-
Kidney or liver problems.
-
Planning for vaccines.
-
Pregnancy and lactation.
Preservation and storage of the drug
-
The drug should be kept in its package away from light before being used.
-
Keep in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2-8 ° C.
-
Don't freeze.
-
Keep out of children's reach.
-
When using Hadlima, it can be stored at room temperature (below 25 ° C), for a maximum of 28 days.
-
Once the medicine is taken out of the refrigerator, it should be used within 28 days even if returned to the refrigerator.
Shippping & Return
xسياسة الاسترجاع والاستبدال
هدفنا في متجر الجواهر هو رضاكم التام 🌸، ونسعى دايمًا نقدم أفضل تجربة تسوق بكل وضوح وعدل. نتعامل مع عملائنا بكل مصداقية، ونتمنى يكون التعامل متبادل بنفس الروح.
في حال تم طلب الإلغاء أو الاسترجاع قبل بدء الشحن، يتم إرجاع المبلغ كامل للعميل.
ويحق للعميل طلب الاسترجاع خلال مدة 3 أيام من تاريخ الاستلام، بشرط:
- أن يكون المنتج غير مستخدم ولم يتم فتحه.
- أن يكون بحالته الأصلية وخالي من أي تلف.
- ألا يكون المنتج من الأصناف المستثناة من الاسترجاع أو الاستبدال.
المنتجات غير القابلة للاسترجاع أو الاستبدال:
- المنتجات التي تحتاج تخزين خاص مثل: أدوية الثلاجة، الحليب، وأغذية الأطفال.
- مزيلات العرق ومنتجات العناية الشخصية والنسائية، إلا في حال وجود عيب مصنعي.
طريقة طلب الاسترجاع أو الاستبدال:
للطلب، يرجى التواصل معنا عبر واتساب على الرقم:
0563649160
في حال طلب الاسترجاع:
بعد التأكيد، يتم إرسال بوليصة شحن للعميل لتسليم المنتج لشركة الشحن وهو بحالته الأصلية.
بعد استلام شركة الشحن للمنتج، يتم إرجاع المبلغ بعد خصم قيمة الشحن خلال مدة من 5 إلى 7 أيام عمل.
في حال طلب الاستبدال:
يتم احتساب قيمة شحن جديدة للطلب البديل.
تنويه مهم:
في حال وصول المنتج بشكل خاطئ من شركة الشحن (باستثناء أدوية الثلاجة، الحليب، وأغذية الأطفال) أو تم إرسال منتج غير صحيح من صيدلية الجواهر المميز، يرجى التواصل مع خدمة العملاء، وبعد التأكد من المشكلة سيتم إرجاع المبلغ كاملًا بعد تسليم المنتج لشركة الشحن.
في حال وصول المنتج مفتوح أو مستخدم أو بحالة غير التي تم شحنه بها، سيتم إلغاء طلب الاسترجاع.
في حال كان الخطأ من شركة الشحن أو تم إرسال منتج خاطئ، نتحمل تكلفة إرسال المنتج لفرع شركة الشحن عبر تطبيقات التوصيل بحد أقصى 20 ريال، في حال كان الفرع بعيد.
في حال عدم استلام العميل للطلب وعودة الشحنة لنا، يتم إرجاع المبلغ بعد خصم قيمة الشحن، وإذا رغب العميل بإعادة الشحن مرة أخرى يتم دفع قيمة شحن جديدة.
You may also like!
Recently Viewed Products
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
